Introduction
Ringworm is one of the leading contagious infections caused by fungi. The fungi that cause ringworm are known as dermatophytes. There are different names of fungi depending on the host they infect. Anthropophilic fungi infect human skin while zoophilic fungi infect animals. Geophilic fungi dwell in soil. Ringworm can pass from one person to another through different ways. The common methods of infection include direct contact with infected people, domesticated animal, soil, and objects. The three types of fungi produce spores that can infect people. However, anthropophilic dermatophytes normally infect the surface of human skin. In most cases, anthropophilic dermatophytes are unlikely to trigger responses from the immune system. Zoophilic and geophilic fungi produce inflammatory responses inside the skin.
Tinea Capitis
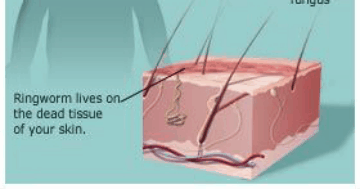
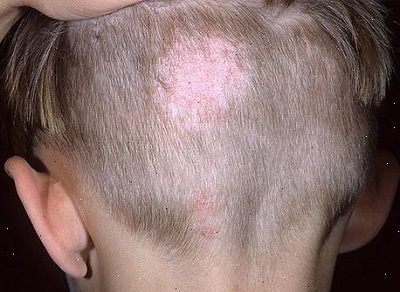 This type of ringworm occurs on the skin that covers the head or the scalp. Persons with this type of ringworm have a number of symptoms including round and itchy patches on the head. These patches are usually reddish in color. These patches grow with time and are likely to become scaly. Hairs in the infected areas become brittle and start falling off. As a result, circular patches with no hair appear on the head. This type of ringworm is extremely infectious and mainly occurs in School-going children. The common methods of contacting Tinea Capitis include direct contact with infected persons or pets.
This type of ringworm occurs on the skin that covers the head or the scalp. Persons with this type of ringworm have a number of symptoms including round and itchy patches on the head. These patches are usually reddish in color. These patches grow with time and are likely to become scaly. Hairs in the infected areas become brittle and start falling off. As a result, circular patches with no hair appear on the head. This type of ringworm is extremely infectious and mainly occurs in School-going children. The common methods of contacting Tinea Capitis include direct contact with infected persons or pets.
Tinea Cruris
This type of ringworm is also known as the jock itch. Tinea Cruris manifests in the form of a red and itchy rash around the groin. This rash usually has well-established edges. The fungus that causes this condition prefers moist and dark parts. It also takes advantages of the creases that appear on top of human thighs and buttocks. These areas are usually sweaty because they have many sweat glands compared to other body parts. The high rate of perspiration in these areas creates an ideal environment for the fungus to grow. Synthetic and tight underclothes also enable the fungus to flourish by inhibiting the flow of air, which leads to high levels of moisture in these areas. Infection rates are high in males compared to females. Moreover, Tinea Cruris is likely to occur in adult males and adolescents compared to other groups.
Tinea Pedis
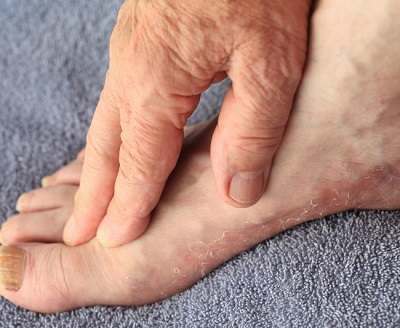 This ringworm is also called athlete’s foot because it infects the feet. Persons with this ringworm have rashes between their toes where there is moisture. These rashes mainly occur in the small toes, but they can also infect other parts of the feet. Tinea Pedis causes itching and a burning effect. Synthetic socks and occlusive shoes can worsen the situation because they trap moisture.
This ringworm is also called athlete’s foot because it infects the feet. Persons with this ringworm have rashes between their toes where there is moisture. These rashes mainly occur in the small toes, but they can also infect other parts of the feet. Tinea Pedis causes itching and a burning effect. Synthetic socks and occlusive shoes can worsen the situation because they trap moisture.
The common sources of this condition include communal swimming pools, community steam rooms, public showers, and health clubs.
Tinea Corporis
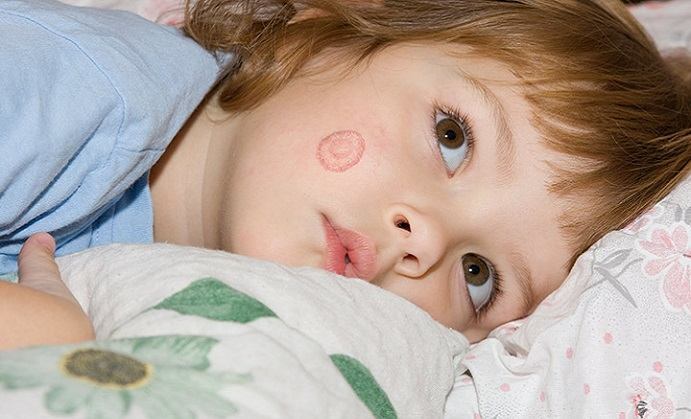
This ringworm infects the body. The fungi that cause Tinea Corporis live under the skin. It causes a round and itchy rash. The rash is usually reddish and the center part of the round area is usually lighter than other parts of the ring. Several rashes may occur. This type of ringworm is extremely infectious and the major sources of infection include humans, soil, animals, and infected objects.
Do you want to find an effective Ringworm treatment? Check out our top rated Ringworm products